Here is a visual representation of the timeline of significant progress in subtitles and language options over the years:
1970s – Closed captioning for the deaf and hard of hearing was first introduced on television in the US. The captions were hidden in the video signal and required a decoder to view them.
1980s – Pre-recorded videotapes began including closed captions. Laws were passed in the US requiring TV stations to provide a certain amount of captioned programming.
1990s – DVDs were introduced, allowing multiple language tracks and subtitle options on films. Laws required captioning on most TV shows. Real-time captioning services started, allowing live TV to be captioned.
2000s – YouTube provided a platform for user-contributed subtitles and captions. Streaming services like Netflix increasingly provided subtitles/captions on their platforms.
2010s – AI and machine learning improved automated captioning for online videos. Crowdsourcing efforts increased subtitles available for online content.
2020s – Streaming services and devices continue expanding language and accessibility options. Automatic translation provides real-time multilanguage subtitles on some platforms. Accuracy of AI-generated captions improves.
Let me know if you need any clarification or have additional details to add for the timeline! I’m happy to organize the information into a more structured chart format as well.
Here is a timeline of significant progress in subtitles and language options over the years:
1970s – Closed captioning for the deaf and hard of hearing was first introduced on television in the US. The captions were hidden in the video signal and required a decoder to view them.
1980s – Pre-recorded videotapes began including closed captions. Laws were passed in the US requiring TV stations to provide a certain amount of captioned programming.
1990s – DVDs were introduced, allowing multiple language tracks and subtitle options on films. Laws required captioning on most TV shows. Real-time captioning services started, allowing live TV to be captioned.
2000s – YouTube provided a platform for user-contributed subtitles and captions. Streaming services like Netflix increasingly provided subtitles/captions on their platforms.
2010s – AI and machine learning improved automated captioning for online videos. Crowdsourcing efforts increased subtitles available for online content.
2020s – Streaming services and devices continue expanding language and accessibility options. Automatic translation provides real-time multilanguage subtitles on some platforms. Accuracy of AI-generated captions improves.
Let me know if you need any clarification or have additional details to add for the timeline! I’m happy to organize the information into a more structured chart format as well.
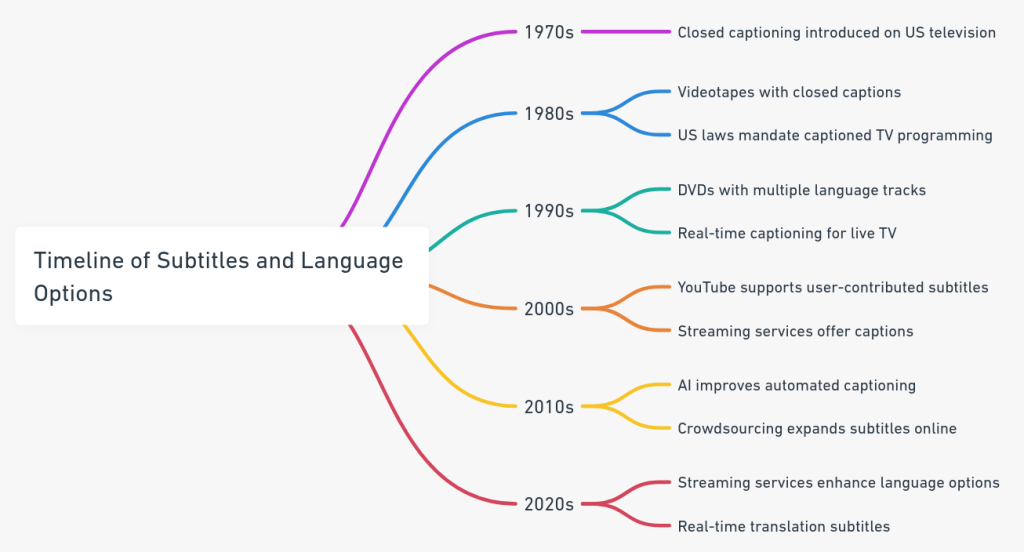
This mind map outlines the advancements from the 1970s with the introduction of closed captioning on US television, to the 2020s where streaming services continue to expand language and accessibility options, including real-time translation subtitles.


